The on-site search feature uses titles, headings, descriptions, and taxonomy to provide score-based search results to users.
With JavaScript enabled, the search tool downloads a data file for the search and provides an instant search as users type.
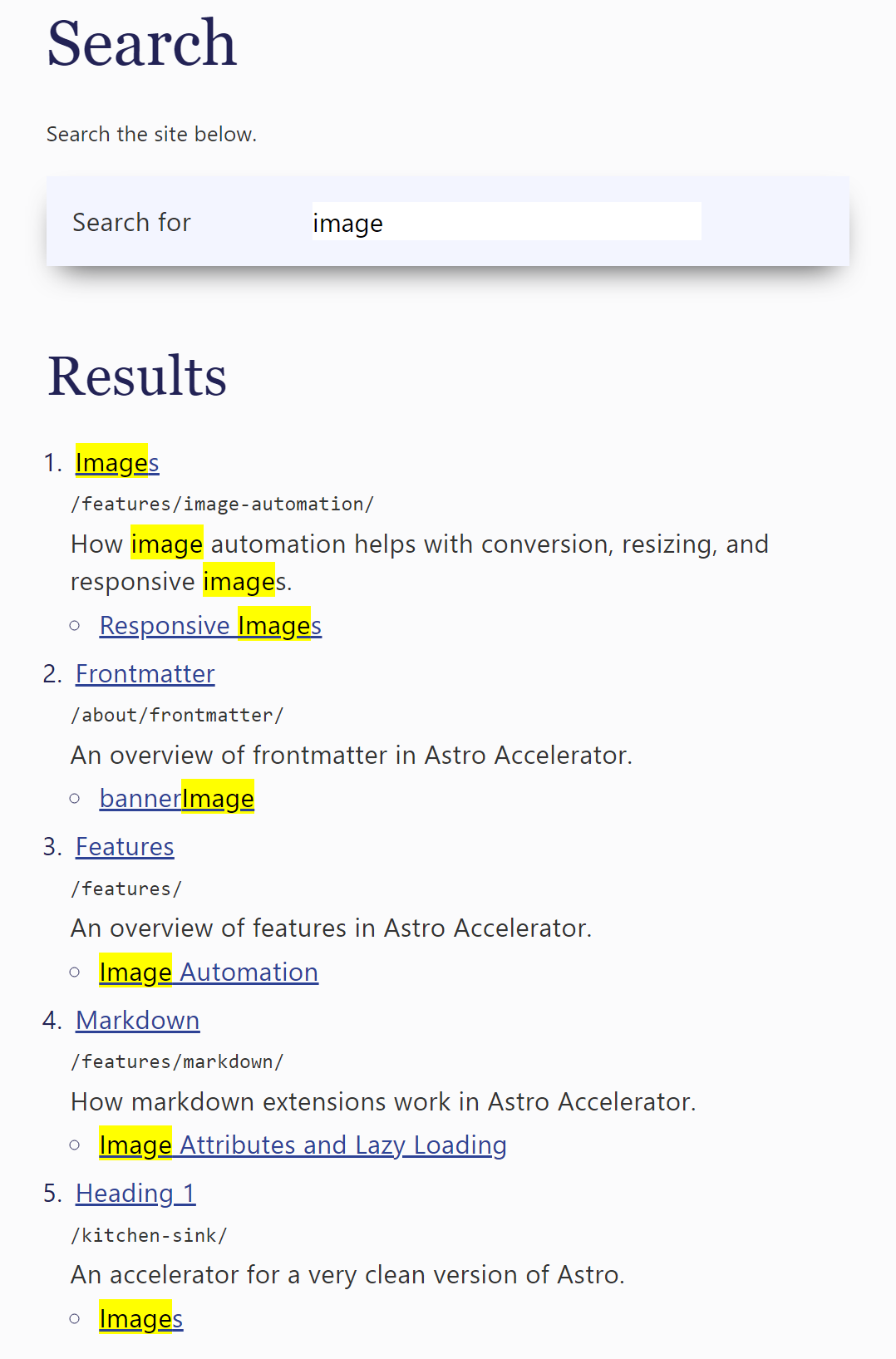
The results list shows:
- The title of the result pages
- The relative path to the page
- The frontmatter description
- Matching sub-headings for quick navigation to the page section
Matching text is highlighted using the HTML <mark> element.
Search page
You should have a page on your site that uses the search layout:
layout: src/layouts/Search.astroThis page will be found and linked from the search icon.
You can place markdown content in your search page that will appear above the search form.
Search dialog
You can enable a search dialog, which will open a modal dialog to perform the search without leaving the page.
This is enabled with the search feature flag.
When enabled, the search can be opened by clicking on the element with the class “search-icon” or using CTRL + SPACE.
Search data
The search URLs in search.json are fully qualified, which means you can ingest the data into an alternative search technology.
For example, you could read this file into elastic search or a similar technology.
Synonyms
You can catch typos, alternate spellings, initialisms, differences between British and American English using the synonyms file.
Add a JavaScript file called /public/js/synonyms.js (next to the search.js file) to switch search terms where necessary. For example, to change “licence” to “license”, or “cod” to “call of duty”.
The file uses a simple dictionary:
const synonyms = {
"cod": "call of duty",
"licence": "license"
};
export { synonyms };Synonyms are added to the search, rather than replaced.
If the file is empty or does not exist, no action will be taken.
Fallback search
In the event of JavaScript being disabled or a transient error, the search falls back to a search engine. This is configurable in config.ts.
search: {
fallbackUrl: 'https://www.google.com/search',
fallbackSite: 'q',
fallbackQuery: 'q',
},For example, the search will fallback to Google with the query:
site:https://astro.stevefenton.co.uk/ imageTrying out different scoring systems
The scoring system is currently part of the search script:
var scoring = {
depth: 5,
phraseTitle: 60,
phraseHeading: 20,
phraseDescription: 20,
termTitle: 40,
termHeading: 15,
termDescription: 15,
termTags: 15,
termKeywords: 15
};This is likely to be made customizable in the future.
You can test out different scoring weights by overriding entries with a query string.
For example, to override the depth score (currently 5 points per level bonus to shallower paths) you can pass the querystring ?s_depth=10. You can pass any of the scoring items, by prefixing them with s_, such as s_depth, s_phraseTitle, or s_termTags.